Video
Website users will find more information about the topic in a short and informative video

End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture.

Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages.

Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls.

Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all.

Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable.

Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns.

Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts.

Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development.

Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss.
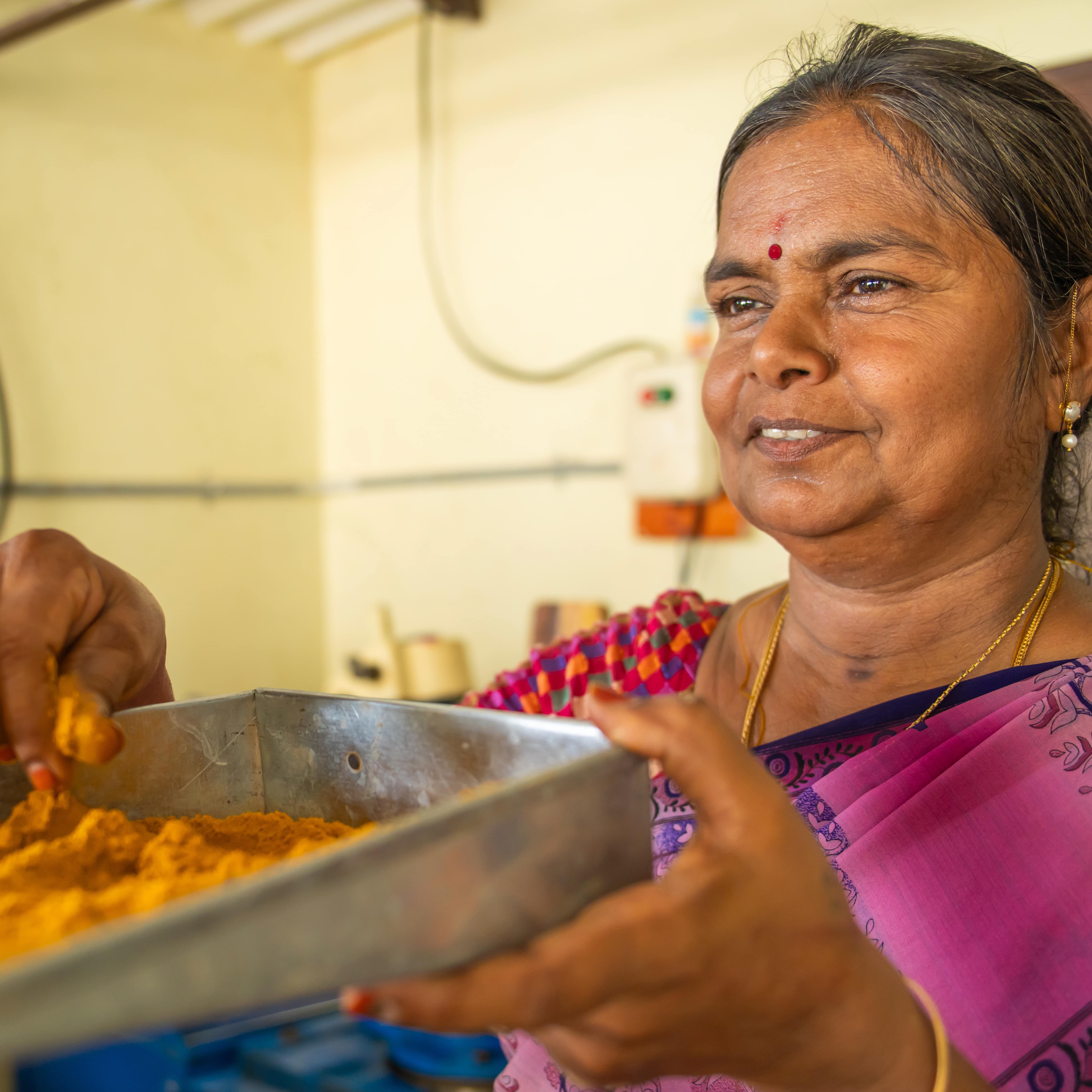
Biodiversity is the variety of life in all its forms, including the diversity of species, ecosystems, and genetic variations within species. For India and Germany, protecting biodiversity is a national priority as it is essential for healthy environments, human well-being, and sustainable development. It provides crucial goods and services like food, fuel, and climate regulation, as well as pollination, water, flood, and storm protection. Although India covers only 2.4% of the world's land area, it is home to over 7% of the world's recorded species and 18% of the global human population.
India and Germany support the conservation and productive potential of biodiversity to sustain the livelihoods for future generations. Central to our partnership is the delivery of high-quality ecological and economic solutions to public and private partners, promoting participatory conservation and management practices. Our joint ambitions focus on preserving the rich biodiversity, enhancing ecosystem services, and supporting natural resource-dependent communities.
The Indo-German cooperation on biodiversity aligns closely with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the United Nations, the Convention on Biological Diversity, and the Paris Agreement on climate change. By advocating sustainable practices, building local capacities, and integrating biodiversity into sectoral development strategies, the GSDP contributes significantly to SDGs related to life on land (SDG 15), life below water (SDG 14) and climate action (SDG 13).
Biodiversity conversation is crucial to achieve the goals of the Paris Agreement. It supports climate mitigation through carbon sequestration and ecosystem resilience. This is essential for stabilising global temperatures. Additionally, biodiverse ecosystems provide vital ecosystem services that aid in climate adaptation, such as coastal protection, water retention, and sustainable agriculture. Integrating biodiversity conservation into national climate strategies not only enhances resilience but also promotes sustainable development. This special connection is one of the main reasons why India and Germany are prioritising biodiversity as one of the main areas of collaboration under the GSDP.